SLODAR
Menu
Get in touch
- [email protected]
- +44(0)191 3342277
- Centre for Advanced Instrumentation
Department of Physics
University of Durham
South Road
Durham
DH1 3LE
SLODAR
Durham University CfAI developed the SLODAR (SLOpe Detection And Ranging) technique for characterisation of the vertical profile of atmospheric optical turbulence.
SLODAR is a crossed beams method based on observations of double stars using a Shack-Hartmann wavefront sensor. The optical turbulence profile (OTP) is recovered from the cross-correlation of the wavefront slope measurements for the two stars.
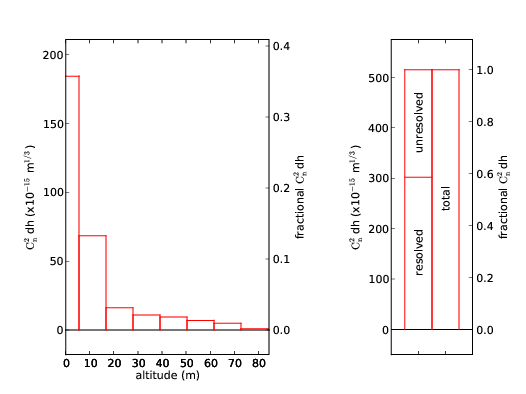
Conventional SLODAR can provide measurements of the turbulence profile for the whole atmosphere. Here we present a new implementation of the technique to enable profiling with very high resolution of the surface layer turbulence (only) by observing targets with very large angular separations. These widely separated targets cannot be observed simultaneously within the field of view of a single WFS. Hence, we use a reflective wedge to divert the light for the two target stars into separate WFSs with independent detectors. With this modification, a vertical resolution of ∼10 m was achieved, and the surface layer of turbulence was resolved. We refer to the modified technique as surface-layer SLODAR or SL-SLODAR.
https://academic.oup.com/mnras/article/406/2/1405/1005211

at Paranal (Photo: Tim Butterley)
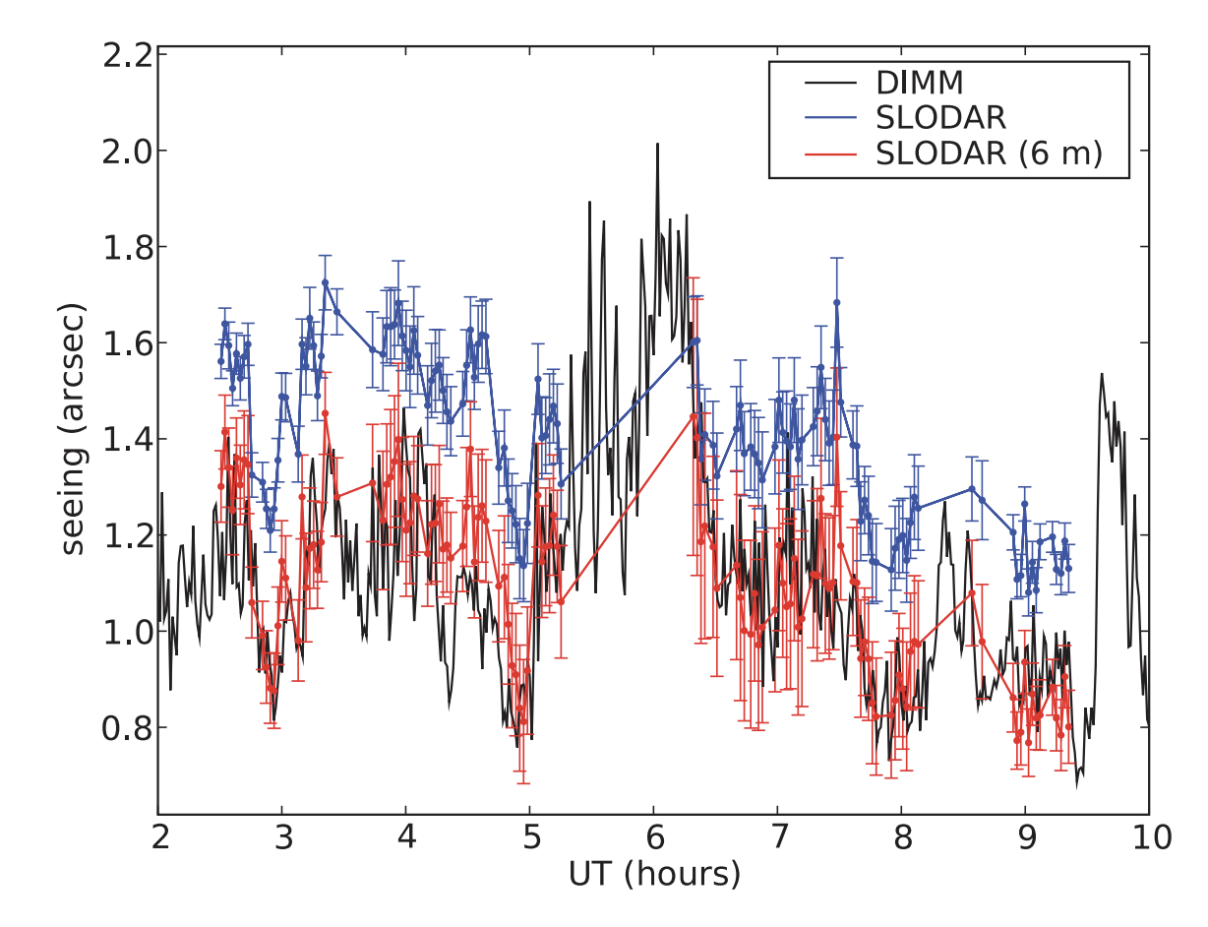
DIMM.
